

| Course Number: | 2000310 |
|---|---|
| Course Title: | AL: English 1 |
| Course Section: | Grades PreK to 12 Education Courses |
| Abbreviated Title: | ALC - English 1 |
| Number of Credits: | One credit (1) |
| Course Length: | Year (Y) |
| Course Level: | 2 |
| Course Status: | Course Approved |
| General Notes: |
Laboratory investigations that include the use of scientific inquiry, research, measurement, problem solving, laboratory apparatus and technologies, experimental procedures, and safety procedures are an integral part of this course. The National Science Teachers Association (NSTA) recommends that at the high school level, all students should be in the science lab or field, collecting data every week. School laboratory investigations (labs) are defined by the National Research Council (NRC) as an experience in the laboratory, classroom, or the field that provides students with opportunities to interact directly with natural phenomena or with data collected by others using tools, materials, data collection techniques, and models (NRC, 2006, p. 3). Laboratory investigations in the high school classroom should help all students develop a growing understanding of the complexity and ambiguity of empirical work, as well as the skills to calibrate and troubleshoot equipment used to make observations. Learners should understand measurement error; and have the skills to aggregate, interpret, and present the resulting data (National Research Council, 2006, p.77; NSTA, 2007).
|

Overview of AL: English I
In AL: English I, provide instruction in the Language Arts strands of the reading process, literary analysis, writing process, writing applications, communication, and information and media literacy. It offers instruction in reading and vocabulary strategies necessary for comprehension of printed materials; research; the writing of effective paragraphs and multipara graph papers, with emphasis upon all stages of the writing process in timed and untimed assessments (prewriting, drafting, revising, editing, publishing); speech instruction including formal and informal presentations; evaluation of mass media; the analysis of genres and the study of language in conjunction with writing, concentrating on conventions of grammar, usage, and mechanics. Technology is incorporated into all aspects of the course. To successfully pass and complete this course, learners must read, watch, and interact with all course materials and components.
How long will this take?
Ask your community coordinator for details on your approximate completion time.
Credit Value: 1.0
Course content must be fully graded to be considered complete.
Grading Scale
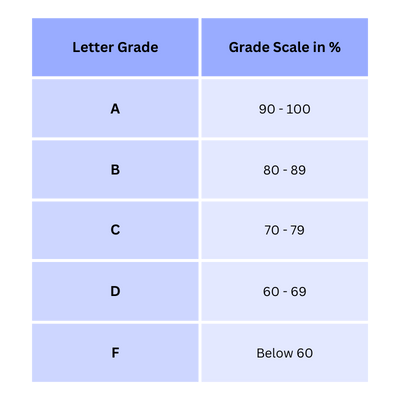
The following will be covered in the Units of this Course:
Unit 1
Unit 2
Unit 3
Unit 4
Unit 5
Unit 6

Unit 1: Using Technology- Navigating the Internet

Unit 1: Using Technology—Navigating the Internet
Unit Focus
Reading
Writing
Organize information using appropriate systems.
Language
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)

Unit 2: Reading - Improving a Skill for Life
Unit 2: Reading—Improving a Skill for Life
Reading
Language
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)

Unit 3: Writing - Making Words Speak
Unit 3: Writing—Making Words Speak
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)

Unit 4: Writing—Using Strategies to Fine-Tune Writing
Unit 4: Writing—Using Strategies to Fine-Tune Writing
Unit Focus
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)

Unit 5: Listening, Viewing, Speaking Communicating Face to Face
 Unit 5: Listening, Viewing, Speaking, Communicating Face to Face
Unit 5: Listening, Viewing, Speaking, Communicating Face to Face
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)

Unit 6: Literature—Discovering the World, Discovering Ourselves
Unit 6: Literature—Discovering the World, Discovering Ourselves
Unit Focus
Reading
Listening, Viewing, Speaking
Language
Literature
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)