Unit 6: Introduction to the Atom
Unit 6: Introduction to the Atom

Unit 6: Introduction to the Atom
Unit 6: Introduction to the Atom
1. Subatomic Particles:
2. Nucleus:
3. Electron Cloud:
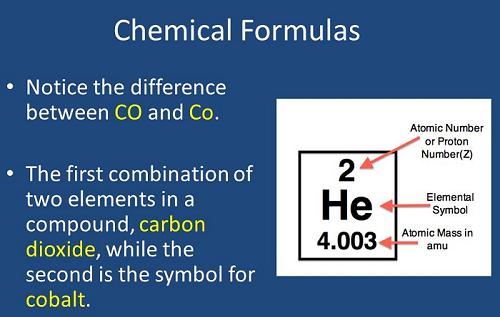
4. Atomic Number (Z):
5. Mass Number (A):
6.  Isotopes:
Isotopes:
7. Electron Shells:
8. Elemental Symbols:
9. Atomic Size:
10. Chemical Behavior:
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)