Unit 10: X or (X, Y) Marks the Spot!
Unit 10: X or (X, Y) Marks the Spot!

Overviews
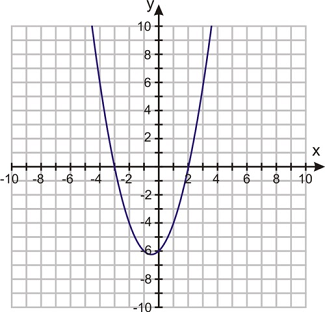
Unit 10: X or (X, Y) Marks the Spot!
This unit shows students how to solve equations algebraically and graphically.
Unit Focus
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Real and Complex Number Systems
- Use the zero product property of real numbers in various contexts to identify solutions to equations.
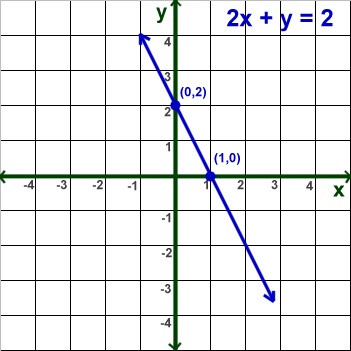 Linear Equations and Inequalities
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Identify and apply the distributive, associative, and commutative properties of real numbers and the properties of equality.
- Symbolically represent and solve multi-step and real-world applications that involve linear equations and inequalities.
- Graph a linear equation or inequality in two variables with and without graphing technology. Write an equation or inequality represented by a given graph.
- Use a graph to approximate the solution of a system of linear equations or inequalities in two variables with and without technology.
- Solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables using graphical, substitution, and elimination methods.
- Solve real-world problems involving systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables.
Polynomials
- Factor polynomial expressions.
Quadratic Equations
- Solve quadratic equations over the real numbers by factoring and using the quadratic formula.
- Use quadratic equations to solve real-world problems.
Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving
- Use various problem-solving strategies, such as drawing a diagram, making a chart, guessing- and checking, solving a more straightforward problem, writing an equation, working backward, and creating a table.
- Decide whether a solution is reasonable in the context of the original situation.
- Decide whether a given statement is always, sometimes, or never factual (statements involving linear or quadratic expressions, equations, inequalities, rational or radical expressions, or logarithmic or exponential functions).
Vocabulary
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 1: Quadratic Equations

Lesson Overview
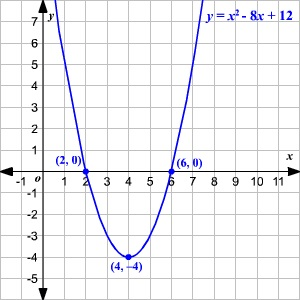
Lesson 1: Quadratic Equations
In this unit, we will expand our problem-solving knowledge to find solutions to various equations, inequalities, systems of equations, and real-world situations.
Reading Process Strand
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Real and Complex Number Systems
- Use the zero product property of real numbers in various contexts to identify solutions to equations.
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Identify and apply the distributive, associative, and commutative properties of real numbers and the properties of equality.
- Symbolically represent and solve multi-step and real-world applications that involve linear equations and inequalities.
Polynomials
- Factor polynomial expressions.
Quadratic Equations
- Solve quadratic equations over the real numbers by factoring and using the quadratic formula.
- Use quadratic equations to solve real-world problems.
Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving
- Use various problem-solving strategies, such as drawing a diagram, making a chart, guessing- and checking, solving a more straightforward problem, writing an equation, working backward, and creating a table.
- Decide whether a solution is reasonable in the context of the original situation.
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 2: Systems of Equations

Lesson Overview

Lesson 2: Systems of Equations
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Graph a linear equation or inequality in two variables with and without graphing technology. Write an equation or inequality represented by a given graph.
- Use a graph to approximate the solution of a system of linear equations or inequalities in two variables with and without technology.
- Solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables using graphical, substitution, and elimination methods.
- Solve real-world problems involving systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables.
Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving
- Use various problem-solving strategies, such as drawing a diagram, making a chart, guessing- and checking, solving a more straightforward problem, writing an equation, working backward, and creating a table.
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 3: Graphing Inequalities

Lesson Overview
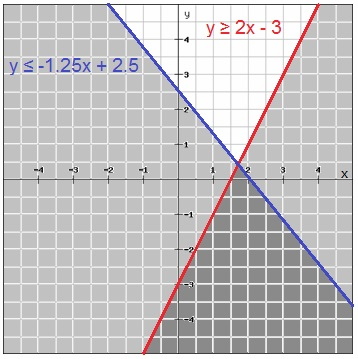
Lesson 3: Graphing Inequalities
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Graph a linear equation or inequality in two variables with and without graphing technology. Write an equation or inequality represented by a given graph.
- Use a graph to approximate the solution of a system of linear equations or inequalities in two variables with and without technology.
- Solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables using graphical, substitution, and elimination methods.
Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving
- Decide whether a given statement is always, sometimes, or never factual (statements involving linear or quadratic expressions, equations, inequalities, rational or radical expressions, or logarithmic or exponential functions).
Lesson Reading
