Unit 4: Making Sense of Rational Expressions
Unit 4: Making Sense of Rational Expressions

Overviews
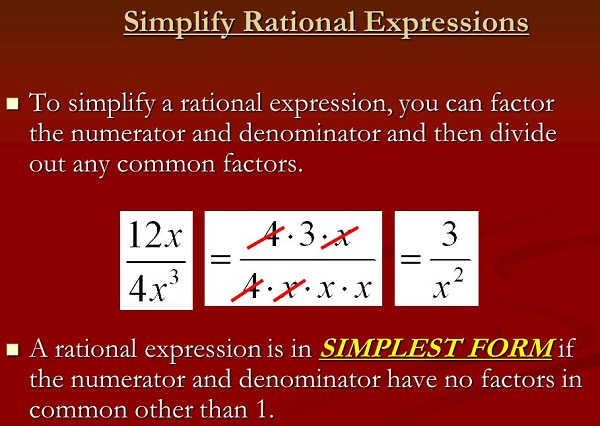
Unit 4: Making Sense of Rational Expressions
This unit emphasizes performing mathematical operations on rational expressions and using these operations to solve equations and inequalities.
Unit Focus
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal, organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Identify and apply the distributive, associative, and commutative properties of real numbers and the properties of equality.
- Solve and graph simple and compound inequalities in one variable and be able to justify each step in a solution.
Polynomials
- Simplify monomials and monomial expressions using the laws of integral exponents.
- Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
- Factor polynomial expressions.
- Divide polynomials by monomials and polynomials with various techniques, including synthetic division.
Vocabulary
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 1: Simplifying Rational Expressions

Lesson Overview
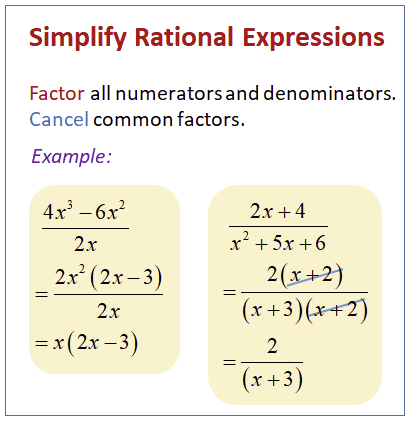
Lesson 1: Simplifying Rational Expressions
Simply rational expressions are algebraic expressions that represent ratios of two polynomial expressions. In simpler terms, they are fractions where the numerator and denominator are both polynomials. These expressions can often be simplified by canceling out common factors between the numerator and denominator, resulting in a reduced form. Simply rational expressions are used extensively in mathematics to model relationships, solve equations, and analyze functions.
- Algebra students must be able to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify rational expressions efficiently. These skills become more critical as you progress in using mathematics. As an algebra student, you can work with methods you need for future mathematical success.
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal, organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 2: Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions

Lesson Overview
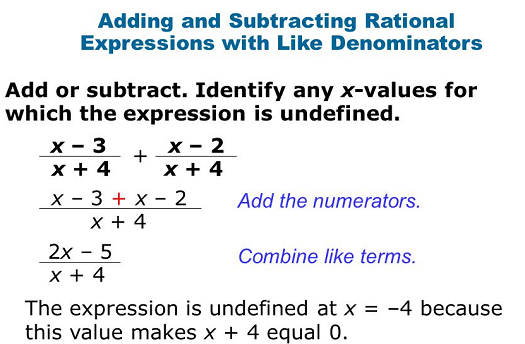
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process Strand
Prewriting
- To develop a personal, organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Polynomials
- Simplify monomials and monomial expressions using the laws of integral exponents.
- Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
- Factor polynomial expressions.
- Divide polynomials by monomials and polynomials with various techniques, including synthetic division.
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 3: Multiplication and Division of Rational Expressions

Lesson Overview

Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal, organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid).
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Polynomials
- Simplify monomials and monomial expressions using the laws of integral exponents.
- Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
- Factor polynomial expressions.
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 4: Solving Equations

Lesson Overview
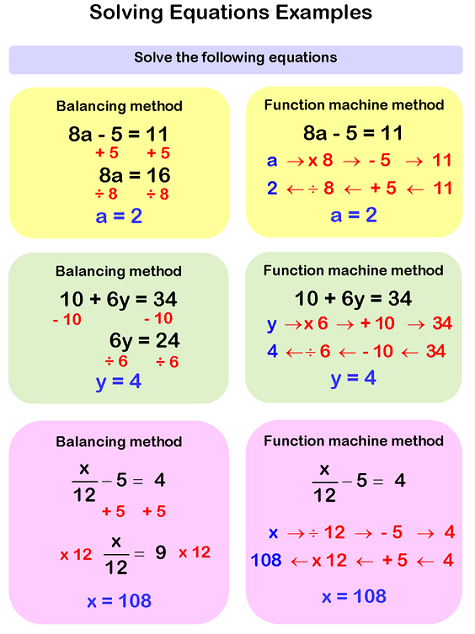
Reading Process
Solving equations involves finding the values of variables that make the equation true. This process typically entails performing a series of mathematical operations to isolate the variable on one side of the equation. The solutions obtained represent the points where the equation's graph intersects the x-axis in a Cartesian coordinate system. Solving equations is a fundamental skill in mathematics and is used in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and computer science, to analyze and predict behavior based on given conditions and relationships.
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
PrewritingTo develop a personal, organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot, and pyramid.
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Identify and apply the distributive, associative, and commutative properties of real numbers and the properties of equality.
Polynomials
- Simplify monomials and monomial expressions using the laws of integral exponents.
- Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
- Factor polynomial expressions.
- Divide polynomials by monomials and polynomials with various techniques, including synthetic division.
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 5: Solving Inequalities

Lesson Overview
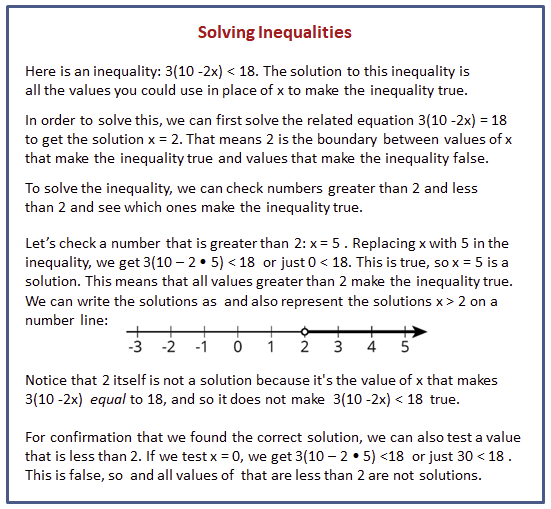
Reading Process
Solving inequalities involves determining the values of a variable that make an inequality true. This process usually includes manipulating the inequality using arithmetic operations to isolate the variable. Unlike equations, inequalities represent a range of possible solutions rather than specific points. The solutions to an inequality are often expressed as intervals or sets of values that satisfy the given conditions. Solving inequalities is essential in mathematics and various real-world scenarios, such as budgeting, optimization, and decision-making processes.
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Writing Process
Prewriting
- To develop a personal, organizational style, the student will prewrite using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, spreadsheet, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid)
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Identify and apply the distributive, associative, and commutative properties of real numbers and the properties of equality.
- Solve and graph simple and compound inequalities in one variable and be able to justify each step in a solution.
Polynomials
- Simplify monomials and monomial expressions using the laws of integral exponents.
- Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
- Factor polynomial expressions.
- Divide polynomials by monomials and polynomials with various techniques, including synthetic division.
Lesson Reading