Unit 6: Extreme Fractions
Unit 6: Extreme Fractions

Overviews
Unit 6: Extreme Fractions
This unit will illustrate the difference between shape and size as they relate to the concepts of congruency and similarity.
Unit Focus
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Radical Expressions and Equations
- Simplify algebraic ratios.
- Solve algebraic proportions.
Vocabulary
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 1: Ratios and Proportions

Lesson Overview
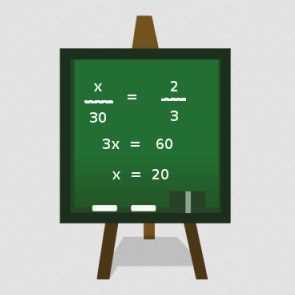
Lesson 1: Ratios and Proportions
We should be able to see that changing the size of a geometric figure can occur without changing the shape of a figure. Working with ratios and proportions will help us understand the relationship between congruence and similarity.
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
Algebra Body of Knowledge
Radical Expressions and Equations
- Simplify algebraic ratios.
- Solve algebraic proportions.
Lesson Reading
Continue to the Next Page
Lesson 2: Similarity and Congruence

Lesson Overview
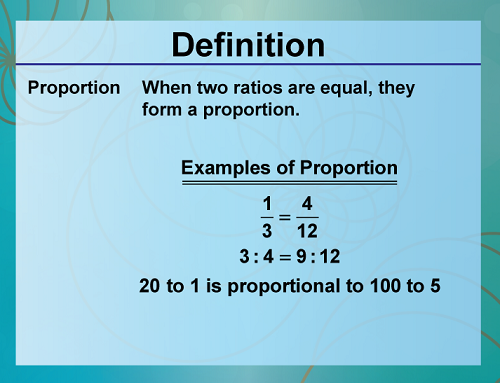
Lesson 2: Similarity and Congruence
Reading Process
Vocabulary Development
- The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly.
- The student will listen to, read, and discuss familiar and conceptually challenging text.
- The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words.
Algebra Body of Knowledge
- Radical Expressions and Equations
- Solve algebraic proportions.
Lesson Reading
