Unit 1: Biology and the Scientific Method
Unit 1: Biology and the Scientific Method

Unit 1: Biology and the Scientific Method
 What is Science?
What is Science?
The Goal of Science
- deals only with the natural world
- to collect and organize information
- propose explanations that can be tested
Science – using evidence to learn about the natural world; a body of knowledge
Science begins with observations – often taking data on what you see, hear, or smell
- data – the information gathered from observations
- quantitative data = numbers
- qualitative data = descriptive
Inference – a logical interpretation based on prior knowledge or experience (Ex. You see a window broken and a baseball on the floor next to the shattered glass. You can -infer- that a baseball broke your window)
Hypothesis – a proposed scientific explanation. This statement is testable and can be confirmed with experimentation or further observation.
Prediction – An if-then statement that shows what you expect to see as a result of an experiment or observation (Ex. If fertilizer makes a plant grow faster, then seedlings planted with fertilizer will be taller than the ones planted without fertilizer)
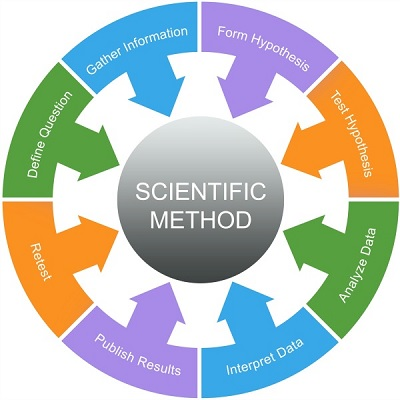
Steps of the Scientific Method
- Ask questions, make observations
- Gather information
- Form a hypothesis
- Set up a controlled experiment
Manipulated variable – the variable that is deliberately changed (independent variable)
Responding variable is variable that is observed ( aka dependent variable - Record and analyze results
- Draw a conclusion
- Repeat
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)
