Unit 3: The Cell - The Basic Unit of Life
Unit 3: The Cell - The Basic Unit of Life

Unit 3: The Cell - The Basic Unit of Life
Unit 3: The Cell - The Basic Unit of Life
A cell is the smallest unit of a living thing and is the basic building block of all organisms.
Objectives:
- State the general characteristics of a cell
Key Points
- A living thing can be composed of either one cell or many cells.
- There are two broad categories of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Cells can be highly specialized with specific functions and characteristics.
Key Terms
Prokaryotic: Small cells in the domains Bacteria and Archaea that do not contain a membrane-bound nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic: Having complex cells in which the genetic material is contained within membrane-bound nuclei.
Cell: The basic unit of a living organism, consisting of a quantity of protoplasm surrounded by a cell membrane, which can synthesize proteins and replicate itself.
Cells as Building Blocks
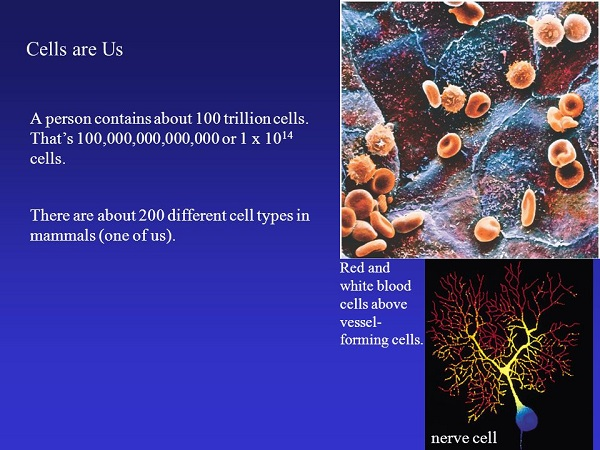
A cell is the smallest unit of a living thing. A living thing, whether made of one cell (like bacteria) or many cells (like a human), is called an organism. Thus, cells are the basic building blocks of all organisms. Several cells of one kind that interconnect with each other and perform a shared function form tissues; several tissues combine to form an organ (your stomach, heart, or brain); and several organs make up an organ system (such as the digestive system, circulatory system, or nervous system). Several systems that function together form an organism (like a human being). There are many types of cells, all grouped into one of two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. For example, animal and plant cells are eukaryotic cells, whereas bacterial cells are prokaryotic.
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)