Unit 4: Cell Growth and Reproduction
Unit 4: Cell Growth and Reproduction

Unit 4: Cell Growth and Reproduction
Unit 4: Cell Growth and Reproduction
Key Concepts:
- The larger a cell becomes, the more demands it places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient at moving nutrients and waste materials across the cell membrane.
- Asexual reproduction is the production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
- Offspring produced by sexual reproduction inherit some genetic information from each parent.
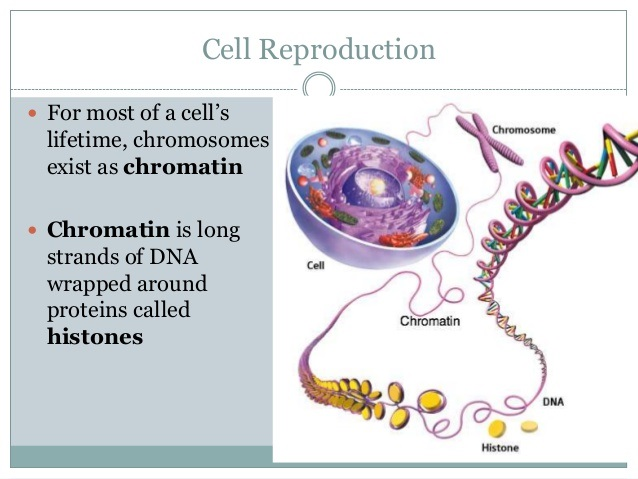
- Chromosomes make it possible to separate DNA precisely during cell division.
- During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells.
- During prophase, the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses. During metaphase,
the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. During anaphase, the chromosomes separate and move along spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. During telophase, the chromosomes, which were distinct and condensed, begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin. - The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins inside and outside the cell.
- Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells. As a result, the cells divide uncontrollably.
- The diploid cells of most adult organisms contain two complete sets of inherited chromosomes and two complete sets of genes.
- In prophase I, replicated chromosomes pair with corresponding homologous
chromosomes. At metaphase I, paired chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. In anaphase I, chromosome pairs move toward opposite ends of the cell. In telophase I, a nuclear membrane forms around each cluster of chromosomes. Cytokinesis forms two new cells. As the cells enter prophase II, their chromosomes become visible. The final four phases of meiosis II result in four haploid daughter cells. - In mitosis, when the two sets of genetic material separate, each daughter cell receives one complete set of chromosomes. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up and then move to separate daughter cells. Mitosis does not normally change the chromosome number of the original cell; meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half. Mitosis produces two genetically identical diploid cells, whereas meiosis produces four genetically different haploid cells.
- Alleles of different genes tend to be inherited from one generation to the next when those genes are located on the same chromosome.
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)
