Unit 13: Weathering and Erosion
Unit 13: Weathering and Erosion
Unit 13: Weather and Erosion
 Unit 13: Weathering and Erosion
Unit 13: Weathering and Erosion
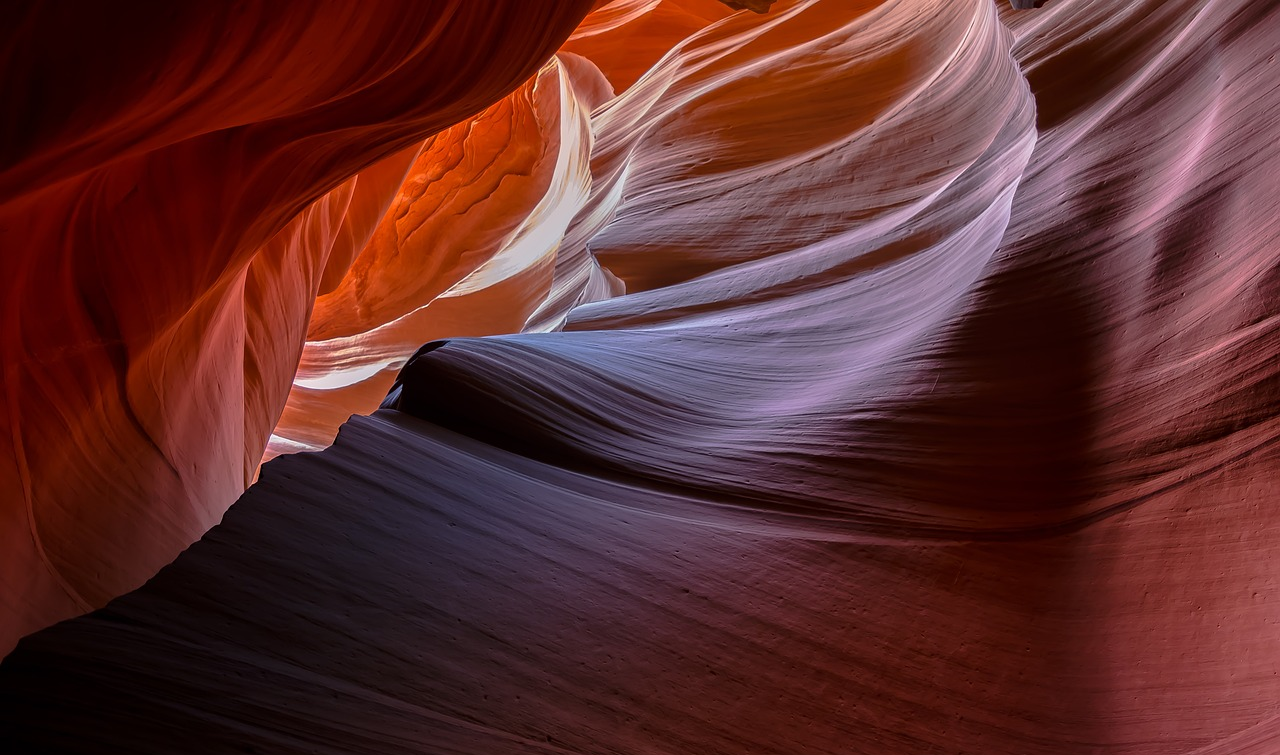
Weathering and erosion are geological processes that work together to shape the Earth's surface by breaking down and transporting materials from one location to another.
Weathering: Weathering is the process by which rocks and minerals are broken down into smaller particles through physical, chemical, and biological processes. There are two main types of weathering:
Mechanical Weathering: Also known as physical weathering, this process involves the physical breakdown of rocks into smaller fragments without changing their chemical composition. Examples of mechanical weathering include frost wedging (expansion of water as it freezes), abrasion (the grinding action of particles carried by wind or water), and exfoliation (peeling away of outer layers of rock due to pressure release).
Chemical Weathering: Chemical weathering involves the alteration of rock minerals through chemical reactions with water, oxygen, acids, and other substances. Examples of chemical weathering processes include hydrolysis (reaction with water), oxidation (reaction with oxygen), and dissolution (dissolving of minerals in water).
Erosion: Erosion is the process by which weathered rock and soil are transported from one place to another by natural agents such as water, wind, ice, and gravity. Erosion occurs when the force of these agents exceeds the resistance of the material being eroded. Common forms of erosion include:
Water Erosion: Water erosion occurs through the action of flowing water, such as rivers, streams, and ocean waves. It can result in the formation of valleys, canyons, and coastal features like cliffs and beaches.
Wind Erosion: Wind erosion occurs when the force of wind lifts and transports particles of soil and sediment. It can lead to the formation of sand dunes, loess deposits, and desert landscapes.
Glacial Erosion: Glacial erosion occurs when glaciers move downhill, carrying and grinding rock material along their path. Glaciers erode valleys, carve out cirques and fjords, and deposit moraines of glacial debris.
Gravity Erosion: Gravity erosion includes mass wasting processes such as landslides, rockfalls, and slumps, where gravity causes the movement of rocks and soil downslope.
Weathering and erosion are fundamental processes in the rock cycle, contributing to the transformation of rocks and the formation of landforms over geological time scales. They are influenced by factors such as climate, geology, topography, vegetation, and human activities. Understanding weathering and erosion is essential for managing natural resources, mitigating hazards, and preserving landscapes and ecosystems.
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)

