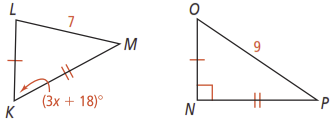Unit 5 Lesson 6 Inequalities in Triangles
Unit 5 Lesson 6: Inequalities in Triangles

Lesson Overview
Inequalities
What You Will Learn
- Inequalities involving angles and sides of triangles
Overview
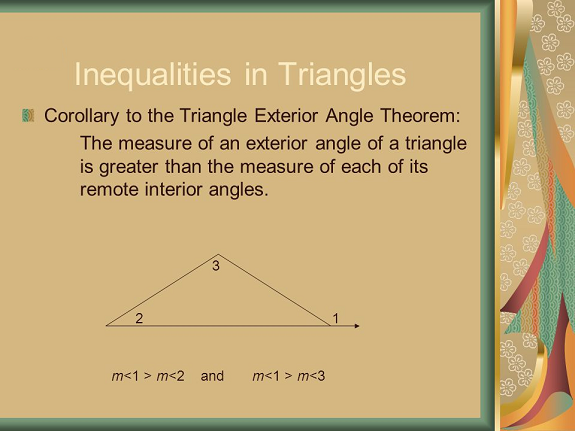
 In this lesson, you will learn to use inequalities involving angles and sides of triangles. So far, you may have noticed that changing the angle formed by two sides of a triangle changes the length of the third side.
In this lesson, you will learn to use inequalities involving angles and sides of triangles. So far, you may have noticed that changing the angle formed by two sides of a triangle changes the length of the third side.
Essential Understanding
The angles and sides of a triangle have unique relationships that involve inequalities.
In triangles with two pairs of congruent sides, there is a relationship between the included angles and the third pair of sides.
- Read pages 234-241 & 242-249 in your course textbook by clicking the textbook icon.
This course is based on a textbook that is viewable by clicking on the textbook icon. Keep the textbook open while you go through the lesson so that you may refer to it throughout the lesson.
Additional Resources
Lesson 6: Inequalities in Triangles
Proceed to the Next Page
Prepare for Application
Instructions
You have now studied Proving Angles Congruent. It is now time to demonstrate your learning.
Try the activities below on your own. You should be able to answer these before beginning the practice.
Do these activities in your journal.
Activity 1
In the figure below, why is it?
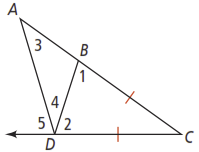
Activity 2
Refer to Problem 2 on page 326 of your textbook.
Suppose the landscape architect wants to place a drinking fountain at the corner with the second largest angle. Which two streets form the corner with the second largest angle?
Activity 3
In the figure below, and . Which side of is the shortest side? Explain your reasoning.
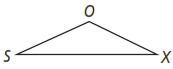
Can a triangle have sides with the given lengths? Explain.
- 2 m, 6 m, and 9 m
- 4 yds., 6 yds., and 9 yds.
1. What inequality relates LN and OQ in the figure below?
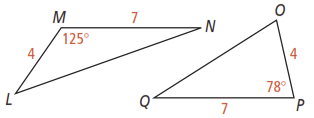
2. In , AB = 3, BC = 4, and CA = 6. In , PQ = 3, QR = 5, and RP = 6. How can you use indirect reasoning to explain why ?
A triangle has side lengths of 4 in. and 7 in.
- What is the range of possible lengths for the third side?
Activity 7
What is the range of possible values for x in the figure below?
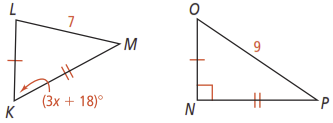
Activity 8
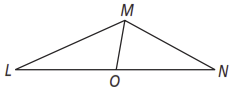
Given: , O is the midpoint of
Prove: LM > MN
Activity 9
What is the range of possible values for x in the figure below?