Unit 8 Lesson 1 The Pythagorean Theorem
Unit 8 Lesson 1: The Pythagorean Theorem

Lesson Overview
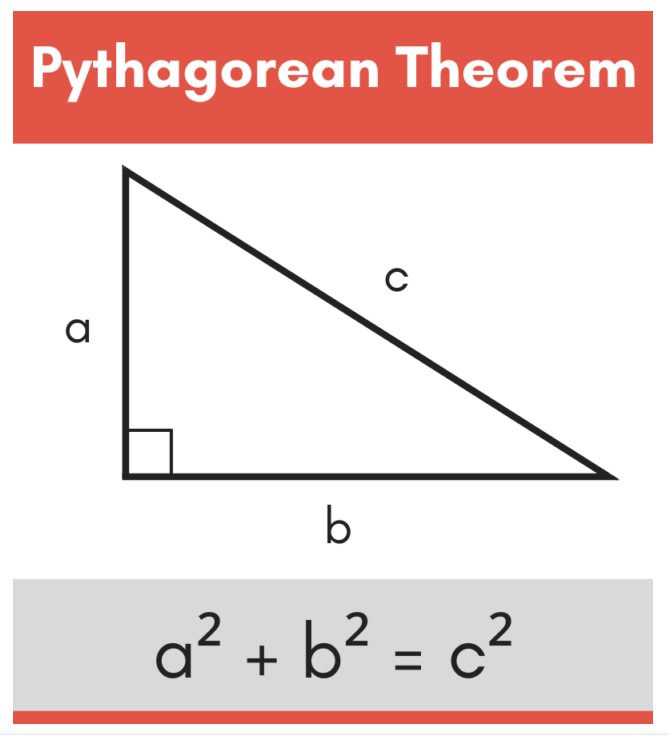
The Pythagorean Theorem
What You Will Learn
- how to use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse.
- finding missing sides of right triangles
- determining whether or not a triangle is acute or obtuse.
Overview
In this lesson, you will learn how to use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. You will show your learning by finding missing sides of right triangles and determining whether or not a triangle is acute or obtuse.
Essential Understanding
If you know the lengths of any two sides of a right triangle, you can find the length of the third side using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Read pages 353-360 in your course textbook.
This course is based on a textbook that is viewable by clicking on the textbook icon. Keep the textbook open while you go through the lesson so that you may refer to it throughout the lesson.
Lesson 1: The Pythagorean Theorem
Proceed to the Next Page
Prepare for Application
Instructions
You have now studied the Constructions of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. It is now time to demonstrate your learning.
Try the activities below on your own. You should be able to answer these before beginning the practice.
Create an extra journal called 'Unit 8: Lesson 1 activities' and do these in your journal.
Activity 1
- The legs of a right triangle have lengths of 10 and 24. What is the length of the hypotenuse?
- Do the side lengths in question 1 form a Pythagorean triple? Explain.
Activity 2
The hypotenuse of a right triangle has a length of 12. One leg has a length of 6. What is the length of the other leg? Express your answer in the simplest radical form.
Activity 3
The size of a computer monitor is the length of its diagonal. You want to buy a 19-in. monitor with a height of 11 in. What is the width of the monitor? Round to the nearest tenth of an inch.
Activity 4
- A triangle has side lengths of 16, 48, and 50. Is the triangle a right triangle? Explain.
- Once you know which length represents the hypotenuse, does it matter which length you substitute for a and which length you substitute for b? Explain.,
Activity 5
Is a triangle with side lengths 7, 8, and 9 acute, obtuse, or right?


