Unit 8 Lesson 3 Trigonometry
Unit 8 Lesson 3: Trigonometry

Lesson Overview
What is Trigonometry?
What You Will Learn
- what are sine, cosine, and tangent ratios
- how to use sine cosine and tangent to determine side lengths and angle measurements in right triangles
Overview
In this lesson, you will learn to use sine, cosine, and tangent ratios to determine right triangles' side lengths and angle measures.
Essential Understanding
Any two right triangles with a pair of congruent acute are similar by the AA Similarity Postulate. Similar right triangles have equivalent ratios for their corresponding sides, called trigonometric ratios. If you know certain combinations of side lengths and angle measures of a right triangle, you can use ratios to find other side lengths and angle measures.
Read pages 368-374 in your course textbook.
This course is based on a textbook that is viewable by clicking on the textbook icon. Keep the textbook open while you go through the lesson so that you may refer to it throughout the lesson.
Lesson 3 Trigonometry
Proceed to the Next Page
Prepare for Application
Instructions
You have now studied Indirect Proof. It is now time to demonstrate your learning.
Try the activities below on your own. You should be able to answer these before beginning the practice.
Create a journal entry called 'Unit 8: Lesson 3 activities' and do these activities in your journal.
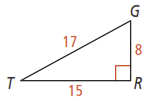
Activity 1
Find the sine, cosine, and tangent ratios in the figure below.
Activity 2
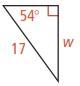
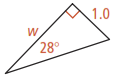
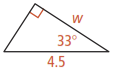
For questions 1-3, find the value of w to the nearest tenth.
1. 
2. 
3. 
- A section of Filbert Street in San Francisco rises at an angle of about 17°. If you walk 150 ft up this section, what is your vertical rise? Round to the nearest foot.
Activity 3
1. Use the figure below. What is to the nearest degree?
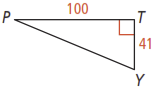
2. Suppose you know the lengths of all three sides of a right triangle. Does it matter which trigonometric ratio you use to find the measure of any of the three angles? Explain.


