Unit 10 Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms and Triangles
Unit 10 Lesson 1: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles
Lesson Overview
Area of Parallelograms
What You Will Learn
- finding the area of parallelograms and triangles using corresponding bases and heights
- finding missing parts and areas of parallelograms and triangles
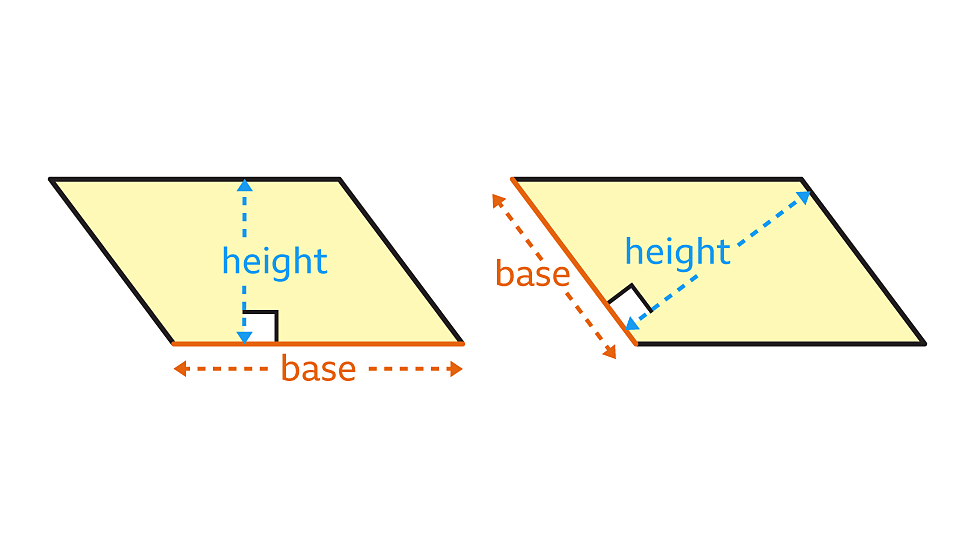
Overview
In this lesson, you will learn to find the area of parallelograms and triangles using corresponding bases and heights. You will show your learning by finding missing parts and areas of parallelograms and triangles.
Essential Understanding
You can find the area of a parallelogram or a triangle when you know its base's length and height.
- Read Pages 409-415 in your course textbook.
This course is based on a textbook that is viewable by clicking on the textbook icon. Keep the textbook open while you go through the lesson so that you may refer to it throughout the lesson.
Lesson 1: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles
Proceed to the Next Page
Prepare for Application
Instructions
You have now studied the Area of Parallelograms and Triangles. It is now time to demonstrate your learning.
Try the activities below on your own. You should be able to answer these before beginning the practice.
Create an extra journal called 'Unit 10: Lesson 1 activities' and do these in your journal.
What is the area of a parallelogram with a base length of 12 m and height of 9 m?
A parallelogram has sides of 15 cm and 18 cm. The height corresponding to a 15-cm base is 9 cm. What is the height corresponding to an 18-cm base?
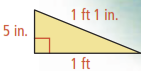
What is the area of the triangle below?
Refer to Problem 4 on page 618 of your textbook. Suppose the base lengths of the square and triangle in the figure above are doubled to 12 in., but the height of each polygon remains the same. How is the area of the figure affected?



