Unit 4: Lesson 3: Temperature
Lesson 3: Temperature

Lesson 3: Temperature
Another vital sign that is commonly measured is body temperature. Body temperature is often recorded to assess whether someone is elevated, which can signal an infection or inflammation, causing a fever. Temperatures that are lower than usual may also indicate health issues. Hypothermia is when the core body temperature drops below the level needed for normal body functioning.
Average human body temperature is known as normothermia, and it is usually around 37° Celsius or 98.6° Fahrenheit for an oral temperature reading. However, body temperature varies depending on several factors, including the location where reading is taken, the time of day, and the person's recent activities. For example, your body temperature is likely the lowest about two hours before you wake up and the highest in the afternoon.
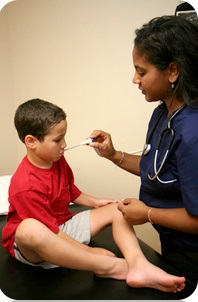
Body temperature is taken using a thermometer. It can be brought in the mouth, armpit, rectum, vagina, ear, and in the gut (by swallowing a thermometer). It can also be assessed by feeling the forehead or the temporal artery on the side of the head or using a plastic thermometer strip at these locations. Since temperature can vary depending on the body location where the thermometer is used, health science professionals need to know the average temperature of the location chosen for the reading. In addition, they need to consider any external factors that can influence the reading. For example, an oral body temperature reading can be affected if the person drank or ate something (cold or hot) recently. An excited person often has a higher body temperature, and someone who is dieting may have a lower body temperature.
Respiratory Rate
The fourth vital sign often measured is the respiratory rate or the number of breaths taken during a specific period. Respiratory rate is often measured as the number of breaths per minute (60 seconds). Typically, respiration rate is measured when a person is at rest, and the breaths are counted by the number of times the chest rises. The respiration rate can also be calculated using a stethoscope.
The average adult respiratory rate is between 12 to 18 breaths per minute. Children typically breathe more often per minute than adults, as their lungs are smaller. For example, newborns may breathe between 20 to 40 times per minute. A person's respiration rate can signal whether the individual has trouble breathing, but studies have indicated that it may not be a good indicator of all respiratory problems. For example, scientists have found that decreased oxygen saturation may not increase breathing rate for all people. Activity, age, and other factors can also affect the rate.
