Unit 1: Scientific Method
Unit 1: Scientific Method

Unit 1: Scientific Method
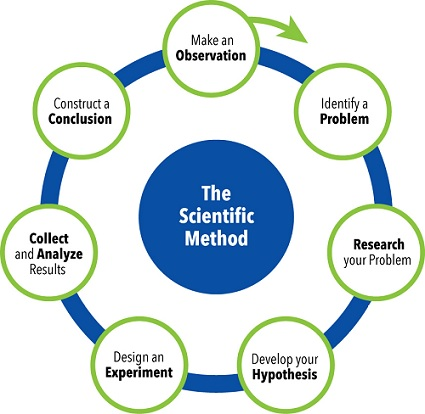
What is the Scientific Method?
The scientific method is an experimentation process to explore observations and answer questions. Does this mean all scientists follow exactly this process? No. Some areas of science can be more easily tested than others. For example, scientists studying how stars change as they age or how dinosaurs digested their food cannot fast-forward a star's life by a million years or run medical exams on feeding dinosaurs to test their hypotheses. When direct experimentation is not possible, scientists modify the scientific method. There are probably as many versions of the scientific method as there are scientists! But even when modified, the goal remains the same: to discover cause and effect relationships by asking questions, carefully gathering and examining the evidence, and seeing if all the available information can be combined into a logical answer.
Even though we show the scientific method as a series of steps, remember that new information or thinking might cause scientists to back up and repeat steps at any point. An iterative process like the scientific method involving such backing up and repeating is called an iterative process.
Whether you are doing a science fair project, a classroom science activity, independent research, or any other hands-on science inquiry, understanding the scientific method's steps will help you focus your scientific question and work through your observations and data to answer the question as well as possible.
Steps of the Scientific Method
- Make an Observation
Scientists are naturally curious about the world. While many people may pass by a curious phenomenon without sparing much thought, a scientific mind will note it as something worth further thought and investigation. - Form a Question
After making an interesting observation, a scientific mind itches to learn more about it. This is a natural phenomenon. If you have ever wondered why or how something occurs, you have been listening to the scientist in you. In the scientific method, a question converts general wonder and interest to a channeled line of thinking and inquiry. - Form a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an informed guess as to the possible answer. The hypothesis may be formed as soon as the question is posed or require much background research and inquiry. The purpose of the hypothesis is not to arrive at the perfect answer to the question but to provide a direction for further scientific investigation. - Conduct an Experiment
Once a hypothesis has been formed, it must be tested. This is done by conducting a carefully designed and controlled experiment. The experiment is one of the most critical steps in the scientific method, as it is used to prove a hypothesis and formulate scientific theories. To be accepted as scientific proof for a theory, an experiment must meet certain conditions – it must be controlled, i.e., test a single variable by keeping all other variables under control. The experiment must also be reproducible to be tested for errors. - Analyze the Data and Draw a Conclusion
As the experiment is conducted, it is essential to note down the results. In any experiment, it is necessary to perform several trials to ensure that the results are constant. The experimenter then analyses all the data and uses it to conclude the strength of the hypothesis. If the data proves the theory correct, the original question is answered. On the other hand, if the data disproves the theory, the scientific inquiry continues by researching to form a new hypothesis and then conducting an experiment to test it. This process continues until a scientific experiment can prove a hypothesis correct.
The whole process is collaborative and is conducted in a documented manner to help other scientists who are doing research in the same field. Throughout history, there have been instances where scientists have stopped their research before completing all the steps of the scientific method, only to have the inquiry taken up and solved by another scientist interested in answering the same question.
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading

