Unit 5: Introduction to the Atom
Unit 5: Introduction to the Atom

Unit 5: Introduction to the Atom
Unit 5: Introduction to the Atom
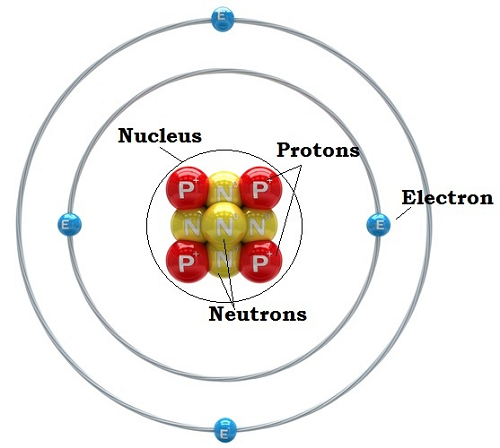
Atoms are the most minor bits of ordinary matter. They are made from particles called protons (which carry a positive electrical charge), neutrons (which have no electrical charge), and electrons (which have a negative electrical charge). The protons and neutrons cluster together in the central part of the atom, called the nucleus, and the electrons 'orbit' the nucleus. A particular atom will have the same number of protons and electrons; most atoms have at least as many neutrons as protons.
An element is a substance made entirely from one type of atom. For example, hydrogen is produced from atoms containing just one proton and one electron. If you had very, very good eyes and could look at the atoms in a sample of hydrogen, you would notice that most of the atoms have no neutrons; some have one neutron, and a few have two neutrons. These different versions of hydrogen are called isotopes. All isotopes of a particular element have the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. If you change the number of protons an atom has, you change its type of element. If you change the number of neutrons an atom has, you make an isotope of that element. All known elements are arranged on a chart called the Periodic Table of Elements.
A compound is a substance made from two or more different elements that have been chemically joined. Some examples of compounds are water (), table salt (NaCl), table sugar (), and chalk ().
A mixture is a substance that combines two or more different materials so that no chemical reaction occurs. A mixture can usually be separated back into its original components. Some examples of mixtures are a tossed salad, salt water, and a mixed bag of M&M's candy.
An atom also contains other particles, called electrons, which orbit the nucleus. These have so little mass that they are ignored when calculating the atomic mass. Electrons have a negative electrical charge that balances with the positive proton charge to create a neutral atom. Given enough energy, however, electrons can sometimes jump away from an atom, ruining the electrical balance and giving the atom a positive charge. Likewise, an atom can sometimes gain an extra electron, giving it a negative charge. Atoms with unbalanced electrical charges, either positive or negative, are called ions. Positive ions — atoms that have lost electrons — are slightly smaller than the original atom, while negative ions — which have gained electrons— are somewhat larger.
Atoms are building blocks. If you want to create a language, you'll need an alphabet. To make molecules, you will need atoms of different elements. Elements are the alphabet in the language of molecules. Each element is a little bit different from the rest.
Why are we talking about elements when this is the section on atoms? Atoms are the general term used to describe pieces of matter. You have billions of billions of atoms in your body. However, you may only find about 40 elements. You will discover billions of hydrogen (H) atoms, billions of oxygen (O) atoms, and many others. All atoms are made of the same essential pieces but are organized in different ways to make unique elements.
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading
Videos and Interactives (Click on Images to View Content)