Unit 8: Chemical Equations
Unit 8: Chemical Equations

Unit 8: Chemical Equations
Unit 8: Chemical Equations
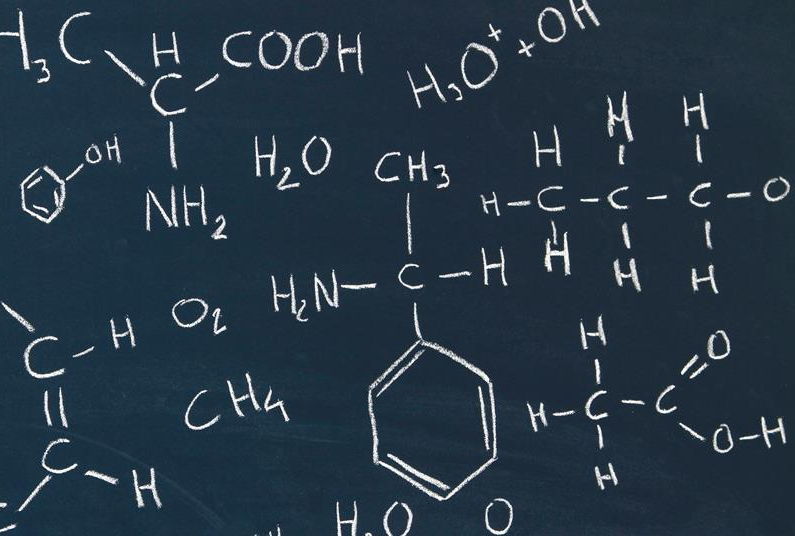
Chemical equations are symbolic representations of chemical reactions. They express the identities and relative quantities of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction. Each chemical species is represented by its chemical formula, and the reaction is depicted by an arrow indicating the direction of the reaction (from reactants to products). Here's a breakdown of the components of a chemical equation:
Reactants: These are the substances that are consumed in the reaction and are written on the left-hand side of the equation.
Products: These are the substances that are formed as a result of the reaction and are written on the right-hand side of the equation.
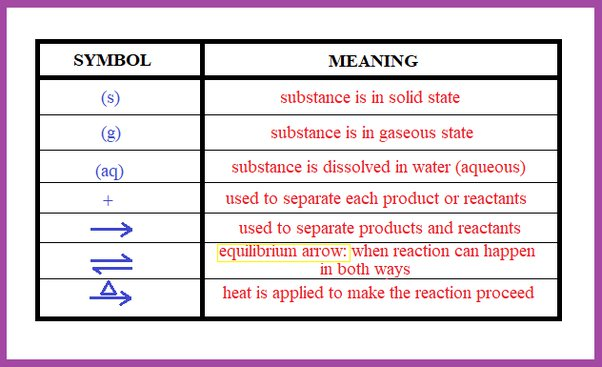
Arrow: The arrow (→) indicates the direction in which the reaction proceeds. It points from the reactants to the products.
Coefficients: These are numbers placed in front of the chemical formulas to indicate the relative quantities of reactants and products. They ensure that the equation obeys the law of conservation of mass.
Chemical reactions happen around us when we light a match, start a car, eat dinner, or walk the dog. A chemical reaction is the process by which substances bond together (or break bonds) and, in doing so, either release or consume energy (see our Chemical Reactions module). A chemical equation is a shorthand that scientists use to describe a chemical reaction. Let's take the response of hydrogen with oxygen to form water as an example. If we had a container of hydrogen gas and burned it in the presence of oxygen, the two gases would react together, releasing energy to form water. To write the chemical equation for this reaction, we would place the substances reacting (the reactants) on the left side of an equation with an arrow pointing to the substances being formed on the right side of the equation (the products). Given this information, one might guess that the equation for this reaction is written as follows:
H + O →
The plus sign on the left side of the equation means that hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) are reacting. Unfortunately, there are two problems with this chemical equation. First, because atoms like to have whole valence shells, single H or O atoms are rare. In nature, hydrogen and oxygen are found as diatomic molecules, H2 and O2, respectively (in forming diatomic molecules, the atoms share electrons and complete their valence shells). Hydrogen gas, therefore, consists of H2 molecules; oxygen gas consists of O2. Correcting our equation, we get the following:
+ →
But we still have one problem. As written, this equation tells us that one hydrogen molecule (with two H atoms) reacts with one oxygen molecule (two O atoms) to form one water molecule (with two H atoms and one O atom). In other words, we seem to have lost one O atom along the way!
Vocabulary
Lesson Reading