Welcome to AL: Consumer Mathematics
Welcome to AL: Consumer Mathematics Class

Overview of AL: Consumer Mathematics
AL: Consumer Mathematics is designed to give learners a practical math course that focuses on managing personal finances and making informed consumer decisions. It covers a wide range of topics essential for everyday life, including budgeting, banking, taxes, loans, investments, insurance, and basic economic principles. Consumer mathematics equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to make sound financial decisions, manage money effectively, and achieve financial goals in everyday life.
To successfully pass and complete this course, learners must read, watch, and interact with all course materials and components.
How long will this take?
Ask your community coordinator for details on your approximate completion time.
Credit Value: 1.0
Course content must be fully graded to be considered complete.
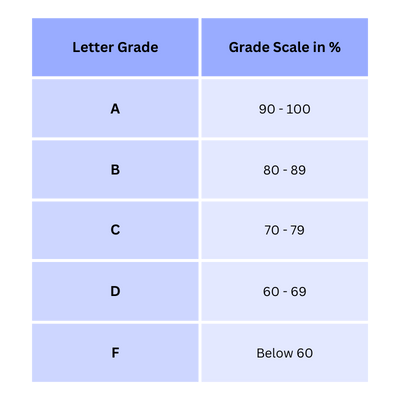
Grading Scale
Course Outline
The following will be covered in the Units of this Course:
Unit 1
Unit 1: Gross Income
- Section 1-1: Calculate straight-time pay.
- Section 1-2: Figure out, overtime, and total pay.
- Section 1-3: Calculate the total hours on a weekly time card.
- Section 1-4: Computer the total pay on a piecework basis.
- Section 1-5: Determine the salary per pay period.
- Section 1-6: Calculate the straight commission and determine the gross pay
- Section 1-7: Compute the total graduated commission.
Unit 2
Unit 2: Net Income
- Section 2-1: Read tables to find the amount withheld for federal income tax.
- Section 2-2: Compute the state taxes on a straight percent basis.
- Section 2-3: Determine the state taxes on a graduated income basis.
- Section 2-4: Work out the amount of income withheld for Social Security and Medicare taxes.
- Section 2-5: Calculate the deduction for group insurance.
- Section 2-6: Figure out net pay per pay period.
Unit 3
Unit 3: Record Keeping
- Section 3-1: Compute the average monthly expenditure.
- Section 3-2: Use records of past expenditures to prepare a monthly budget sheet.
- Section 3-3: Compare amount budgeted to actual expenditures.
Unit 4
Unit 4: Checking Accounts
- Section 4-1: Compute the total checking account deposit.
- Section 4-2: Write a check.
- Section 4-3: Figure out the balance in a check register.
- Section 4-4: Calculate the present balance on a checking account bank statement.
- Section 4-5: Reconcile a check register with a bank account statement.
- Section 4-6: Compute online banking charges and update the check register.
Unit 5
Unit 5: Savings Accounts
- Section 5-1: Complete a savings account deposit slip, and compute the total deposit.
- Section 5-2: Fill out a savings account withdrawal slip.
- Section 5-3: Compute the new balance on a savings account statement.
- Section 5-4: Calculate simple interest.
- Section 5-5: Figure out the compound interest and the amount.
- Section 5-6: Find compound interest using tables.
- Section 5-7: Find interest for daily compounding.
- Section 5-8: Compute the future value of an ordinary annuity and an annuity due.
Unit 6
Unit 6: Cash Purchases
- Section 6-1: Compute the sales tax.
- Section 6-2: Calculate the total purchase price.
- Section 6-3: Figure out the unit price.
- Section 6-4: Find the better buy based on unit price.
- Section 6-5: Work out the final price after using a coupon or rebate.
- Section 6-6: Solve for the dollar amount of the markdown.
- Section 6-7: Compute the sale price when the markdown rate is known.
Unit 7
Unit 7: Charge Accounts and Credit Cards
- Section 7-1: Calculate the new balance on a charge account.
- Section 7-2: Find the finance charge by using the unpaid-balance method.
- Section 7-3: Calculate the finance charge based on the average-daily-balance method where no new purchases are included.
- Section 7-4: Compute the finance charge based on the average-daily-balance method where new purchases are included.
Unit 8
Unit 8: Loans
- Section 8-1: Compute the maturity value and interest rate of a single-payment loan.
- Section 8-2: Calculate the amount financed on an installment loan.
- Section 8-3: Figure out the monthly payment, total amount repaid, and finance charge on an installment loan.
- Section 8-4: Work out the payment to interest, payment to principal, and the new balance.
- Section 8-5: Compute the final payment of a simple interest installment loan.
- Section 8-6: Use a table to find the annual percentage rate of a loan.
Unit 9
Unit 9: Vehicle Transportation
- Section 9-1: Compute the sticker price of a new vehicle.
- Section 9-2: Calculate the dealer’s cost of a new vehicle.
- Section 9-3: Figure out the average retail price of a used vehicle.
- Section 9-4: Use tables to compute the annual premium for vehicle insurance.
- Section 9-5: Compute the total cost per mile of operating and maintaining a vehicle.
- Section 9-6: Calculate the total cost of leasing a vehicle.
- Section 9-7: Figure out the cost per mile of renting a vehicle.
Unit 10
Unit 10: Housing Costs
- Section 10-1: Compute the mortgage loan amount.
- Section 10-2: Determine the monthly payment, total amount paid, and total interest charged.
- Section 10-3: Figure out the total closing costs.
- Section 10-4: Compute the allocation of monthly payment toward principal, interest, and the new principal.
- Section 10-5: Calculate the assessed value and real estate taxes.
- Section 10-6: Work out the amount of coverage.
- Section 10-7: Calculate the annual homeowners insurance premium.
- Section 10-8: Compute the total housing cost and compare it with suggested guidelines.
Unit 11
Unit 11: Insurance
- Section 11-1: Compute health insurance premiums.
- Section 11-2: Calculate the amount the patient pays for health care.
- Section 11-3: Utilize tables to compute the annual premium for term life insurance.
- Section 11-4: Apply tables to data to compute the annual premiums for three types of life insurance.