Chapter 5: Savings Accounts Overview
Chapter 5: Savings Accounts Overview
Overview

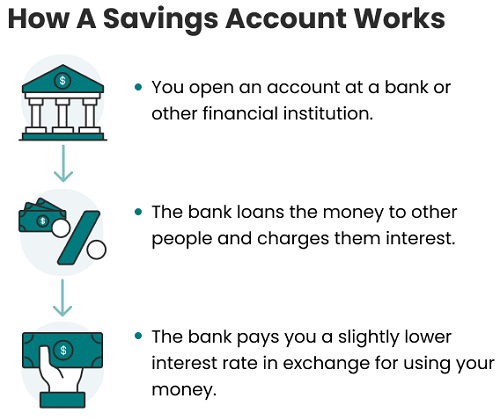 A savings account is a type of bank account specifically designed for storing and growing your savings. Here's an overview of savings accounts:
A savings account is a type of bank account specifically designed for storing and growing your savings. Here's an overview of savings accounts:
Purpose: The primary purpose of a savings account is to help individuals and families save money for future needs and financial goals. It provides a safe and secure place to deposit funds while earning interest on the balance.
Key Features:
Interest Earnings: One of the main features of a savings account is that it allows your money to grow over time through the accrual of interest. The interest rate can vary depending on the bank and the type of savings account.
Safety: Savings accounts are typically insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in the United States, which means that your deposits are protected up to a certain limit (currently $250,000 per depositor, per bank).
Liquidity: Unlike some other types of investments, such as certificates of deposit (CDs) or certain retirement accounts, savings accounts offer easy access to your funds. You can withdraw money from your savings account whenever you need it, although there may be restrictions on the number of withdrawals allowed per month.
Low to No Fees: Many savings accounts have minimal fees, if any. However, some accounts may charge fees for services such as overdrafts, excessive transactions, or account maintenance, so it's essential to review the account terms carefully.
Minimum Balance Requirements: Some savings accounts may require a minimum balance to open the account or to avoid monthly maintenance fees. Be sure to check the account requirements before opening an account.
Online Access: Most banks offer online banking services that allow you to manage your savings account conveniently from your computer or mobile device. This includes checking your balance, transferring funds, setting up automatic transfers, and more.
Uses:
Emergency Fund: Many financial experts recommend keeping an emergency fund in a savings account to cover unexpected expenses, such as medical bills, car repairs, or job loss.
Short-Term Goals: Savings accounts are also suitable for saving for short-term financial goals, such as a vacation, a down payment on a house, or a major purchase.
Long-Term Savings: While savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates compared to other investment options, they provide a safe and stable way to save for long-term goals, such as retirement or education expenses.
Considerations:
Interest Rates: Compare interest rates offered by different banks to find the best savings account for your needs. Some banks offer higher rates or promotional rates for new customers.
Fees and Requirements: Review the account terms, including any fees, minimum balance requirements, and withdrawal limits, before opening a savings account.
Accessibility: Consider how easily you can access your funds and whether you need features such as online banking, mobile banking, or ATM access.
Saving Discipline: A savings account can be an effective tool for saving money, but it requires discipline to regularly contribute to your savings and avoid dipping into the account for non-essential expenses.
Overall, a savings account is a valuable financial tool for building savings, achieving financial goals, and providing financial security. By choosing the right account and being mindful of your saving habits, you can make the most of your savings and work towards a more secure financial future.
In this Unit, you will be covering the following Sections:
Checking Account Video
Unit Sections:
- Chapter 5: Savings Accounts
- Section 5-1: Deposits
- Section 5-2: Withdrawals
- Section 5-3: Account Statements
- Section 5-4: Simple Interest
- Section 5-5: Compound Interest
- Section 5-6: Compound Interest Tables
- Section 5-7: Daily Compounding
- Section 5-8: Annuities
