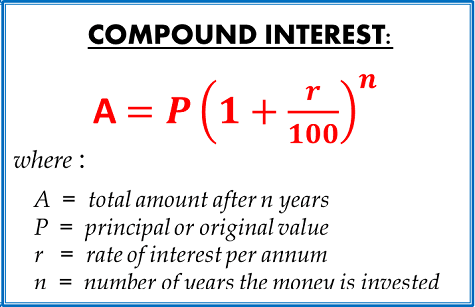
Section 5-5: Compound Interest
Section 5-5: Compound Interest
Overview

 Simple interest is a straightforward method of calculating interest based only on the principal amount of a loan or investment. Here's how simple interest rates work:
Simple interest is a straightforward method of calculating interest based only on the principal amount of a loan or investment. Here's how simple interest rates work:
Principal Amount: The principal amount is the initial sum of money borrowed or invested. For loans, it's the amount borrowed, while for investments, it's the initial amount invested.
Interest Rate: The interest rate is the percentage of the principal amount that is charged or earned as interest over a specific period. It's typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR).
Calculation: To calculate simple interest, you multiply the principal amount by the interest rate and the time period (in years). The formula for calculating simple interest is:
Simple Interest = Principal × Interest Rate × Time
Where:
- Principal = Initial amount of money (loan amount or investment)
- Interest Rate = Annual interest rate (as a decimal)
- Time = Time period for which the interest is calculated (in years)
Example: Let's say you borrow $1,000 at a simple interest rate of 5% per year for 2 years. Using the formula above:
Simple Interest = $1,000 × 0.05 × 2 = $100
In this example, the simple interest on the loan would be $100.
Total Amount: The total amount payable or earned at the end of the term is the sum of the principal amount and the simple interest. For loans, it's the amount to be repaid, while for investments, it's the total amount accumulated.
Total Amount = Principal + Simple Interest
Simple interest rates are commonly used for short-term loans, such as personal loans, car loans, and certain types of investments. They are straightforward to calculate and provide a clear understanding of the interest charges or earnings over the term of the loan or investment. However, it's important to note that simple interest does not account for compounding, which means that the interest is calculated only on the original principal amount and does not accumulate over time.
Online Textbook Read Section 5-5: Compound Interest
