Section 5-8: Annuities
Section 5-8: Annuities
Overview

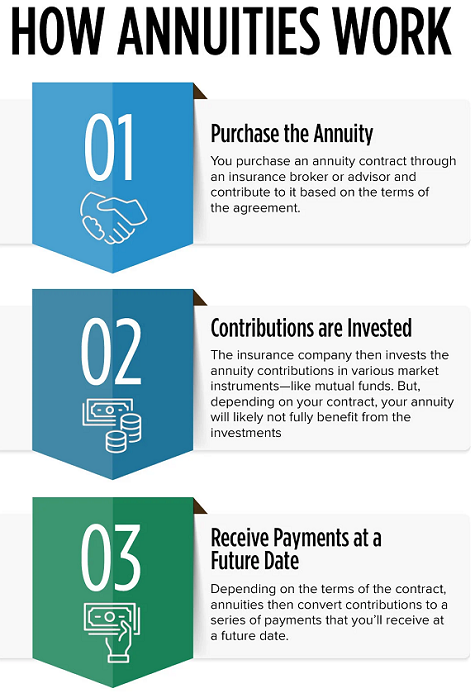 An annuity is a financial product typically offered by insurance companies that provides a series of payments to an individual over a specified period. Annuities are often used as retirement income vehicles, but they can also be used for other purposes, such as long-term savings or wealth accumulation. Here's an overview of annuities:
An annuity is a financial product typically offered by insurance companies that provides a series of payments to an individual over a specified period. Annuities are often used as retirement income vehicles, but they can also be used for other purposes, such as long-term savings or wealth accumulation. Here's an overview of annuities:
Types of Annuities:
- Immediate Annuity: With an immediate annuity, you make a lump-sum payment to the insurance company, and the company begins making regular payments to you immediately (usually monthly or annually).
- Deferred Annuity: With a deferred annuity, you make one or more payments to the insurance company, and the company makes payments to you at a later date (usually after retirement). The payments may be fixed or variable, depending on the type of deferred annuity.
Payment Options:
- Fixed Annuity: In a fixed annuity, the insurance company guarantees a specific interest rate on your investment, and you receive a fixed amount of income for the duration of the annuity period.
- Variable Annuity: In a variable annuity, your payments are tied to the performance of underlying investment options, such as mutual funds. The value of your payments may fluctuate based on the performance of the investments.
- Indexed Annuity: Indexed annuities offer returns based on the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. They typically guarantee a minimum return while also providing the potential for higher returns based on the index performance.
Tax Treatment:
- Annuities offer tax-deferred growth, meaning you don't pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw the money.
- Withdrawals from annuities are generally subject to ordinary income tax, and if you withdraw funds before age 59½, you may also incur a 10% early withdrawal penalty (similar to withdrawals from qualified retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs).
Features and Benefits:
- Guaranteed Income: Annuities provide a reliable source of income, either for a fixed period or for the rest of your life, helping to ensure financial security in retirement.
- Flexibility: Annuities offer flexibility in terms of payment options, including lump-sum withdrawals, periodic payments, or lifetime income streams.
- Death Benefits: Many annuities offer death benefits, allowing your beneficiaries to receive a payout if you pass away before the annuity payments have been exhausted.
- Protection from Market Volatility: Fixed and indexed annuities offer protection from market downturns, providing a level of security for your investment.
Considerations:
- Fees and Expenses: Annuities may come with fees and expenses, such as administrative fees, mortality and expense fees, and investment management fees, which can reduce your overall returns.
- Surrender Charges: Some annuities impose surrender charges if you withdraw funds before a specified period, typically 5 to 10 years.
- Complexity: Annuities can be complex financial products, and it's essential to understand the terms, features, and costs before purchasing one.
- Inflation Risk: Fixed annuities may not keep pace with inflation over time, potentially reducing the purchasing power of your payments in the future.
Annuities can be valuable retirement income tools, providing a stream of income to help meet your financial needs in retirement. However, it's essential to carefully evaluate your options and consider your individual financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance before purchasing an annuity. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you determine whether an annuity is suitable for your needs and circumstances.
Online Textbook Read Section Section 5-8: (Annuities)
